Blog Summary
This article explores the evolution of marketing Eras, from the Production Era to the Experiential Marketing Era. Learn how businesses transitioned from mass production to customer-focused strategies and how digital transformation is shaping modern marketing
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Evolution of Marketing Eras: A Journey Through Time

Marketing eras & Marketing has evolved over the years, adapting to new technologies, consumer behaviours, and business strategies. Understanding the different marketing eras helps businesses align their strategies with modern consumer expectations.
This article explores the key marketing eras, their characteristics, and how they have shaped today’s marketing landscape.
1. The Production Era (Late 1800s–1930s): Focus on Mass Production
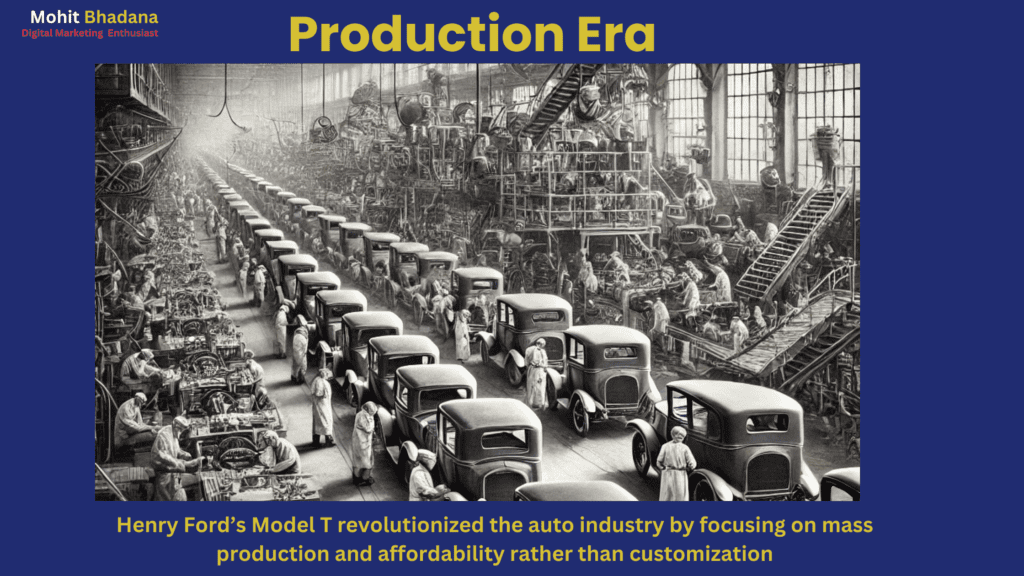
Key Characteristics:
- Emphasis on standardization and mass production.
- Businesses believed that availability alone would drive demand.
- Minimal marketing efforts; companies assumed that “if you build it, they will come.”
Example:
- Henry Ford’s Model T revolutionized the auto industry by focusing on mass production and affordability rather than customization.
Lesson Learned:
- Production efficiency is crucial, but ignoring customer needs can limit growth.
2. The Sales Era (1920s–1940s): Persuasion and Aggressive Selling

Key Characteristics:
- Businesses shifted to aggressive sales techniques to push products.
- Advertising became prominent in newspapers, magazines, and radio.
- Companies focus on creating demand rather than understanding existing needs.
Example:
- Coca-Cola’s Christmas campaign featuring Santa Claus popularized the brand and created a strong emotional connection with consumers.
Lesson Learned:
- Sales techniques work, but without understanding customer needs, long-term brand loyalty is difficult to achieve.
3. The Marketing Era (1950s–1980s): Customer-Centric Approach

Key Characteristics:
- Customer needs became the priority over just selling products.
- Businesses invested in market research and segmentation to tailor products.
- Customization and branding became crucial for differentiation.
Example:
- Apple’s introduction of household personal computers (PCs) addressed consumer needs by making technology accessible to everyday users.
Lesson Learned:
- Understanding the audience and delivering what they want leads to brand loyalty.
Learn more about how Apple revolutionized the pc market
4. The Relationship Era (1990s–2000s): Building Customer Loyalty

Key Characteristics:
- Focus on long-term customer relationships rather than one-time sales.
- The rise of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems.
- Loyalty programs, recurring billing, and upselling & cross-selling became standard business practices.
Example:
- Starbucks’ Rewards Program, which incentivizes repeat purchases and fosters customer loyalty.
Upselling vs. Cross-Selling:
- Upselling: Offering a higher-priced version of a product (e.g., upgrading from a standard coffee to a premium version). Displayed on the product page.
- Cross-selling: Recommending complementary products (e.g., suggesting a pastry when buying coffee). Displayed on the cart page.
Lesson Learned:
- Customer retention is more profitable than acquisition. Investing in relationships builds long-term revenue.
5. The Digital Marketing Era (2000s–Present): Data-Driven Strategies
Key Characteristics:
- Digital marketing tools like SEO, SEM, social media, and email marketing dominate.
- Companies use big data and analytics to target customers effectively.
- Online reviews, influencers, and personalized advertising play a crucial role.
Example:
- Technology-driven marketing strategies, such as targeted ads and automation, help businesses reach their audiences more efficiently.
Lesson Learned:
- Technology enables deeper customer insights, allowing hyper-personalized marketing strategies.
Learn more about Digital marketing and its types
6. The Experiential Marketing Era (Present & Future): Creating Memorable Experiences

Key Characteristics:
- Marketing focuses on customer experiences and emotions.
- Brand storytelling, event marketing, and interactive campaigns are key.
- Companies create immersive experiences to strengthen brand engagement.
Example:
- IKEA showrooms provide an interactive experience where customers can visualize products in real-life setups, enhancing the shopping experience.
Lesson Learned:
- Customers value experiences over just products. Creating emotional connections leads to stronger brand loyalty.
Conclusion
Marketing has evolved from production-focused strategies to customer-centric and technology-driven approaches. Understanding these marketing eras helps businesses adapt and implement effective strategies.
Key Takeaways:
✔ Know your audience – Consumer insights drive success.
✔ Build relationships – Customer loyalty ensures long-term growth.
✔ Leverage digital tools – SEO, social media, and AI optimize engagement.
✔ Create meaningful experiences – Emotional connections boost brand loyalty.
As marketing continues to evolve, staying ahead of trends is crucial for success
FAQs
1. What are the key marketing eras?
The major marketing eras include Production, Sales, Marketing, Relationship, Digital, and Experiential Marketing Eras, each representing a shift in how businesses attract and retain customers.
2. How did the Sales Era differ from the Marketing Era?
The Sales Era focused on pushing products through aggressive selling, while the Marketing Era prioritized understanding customer needs and creating demand through targeted marketing strategies.
3. How has digital marketing changed traditional marketing?
Digital marketing introduced SEO, PPC, social media, and data-driven marketing, allowing businesses to reach targeted audiences more effectively than traditional mass marketing approaches.
4. What is the importance of the Relationship Era?
The Relationship Era emphasized customer retention and loyalty programs, helping businesses build long-term customer relationships rather than focusing solely on new customer acquisition.
5. What is Experiential Marketing?
Experiential Marketing involves creating memorable brand experiences through interactive campaigns, events, and storytelling to forge deeper emotional connections with customers.


